Understanding Rework Underfill Adhesive for Chips: Essential Insights for Optimizing Chip Performance
Rework underfill adhesive plays a vital role in the assembly and reliability of semiconductor chips. As the demand for advanced electronics continues to rise, the necessity for high-performance adhesives that can withstand challenging conditions has become increasingly important. This article will provide an overview of rework underfill adhesives, their properties, and their significance in chip manufacturing.
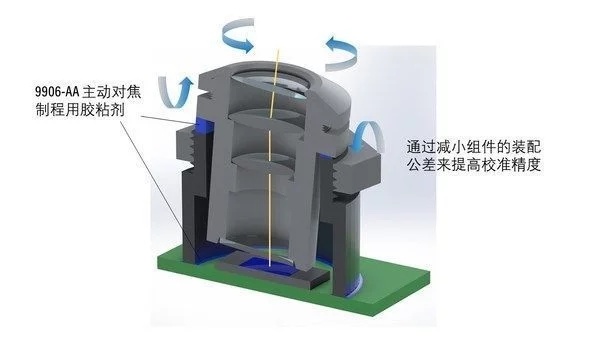
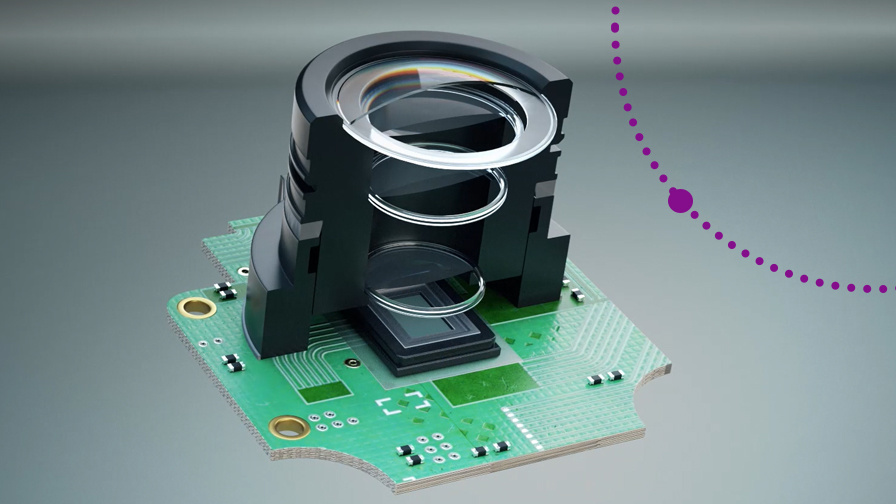
At its core, rework underfill adhesive is designed to support the bond between semiconductor chips and their substrates. This adhesive is particularly crucial during the rework process, which involves repairing or replacing chips without damaging the surrounding components. The ability to remove and replace chips efficiently while maintaining structural integrity is where rework underfill adhesives shine.
One of the primary advantages of these adhesives is their ability to mitigate thermal and mechanical stress. When chips are soldered to substrates, they experience temperature fluctuations and mechanical forces that can lead to delamination or cracking. Rework underfill adhesives provide a protective layer that absorbs these stresses, ensuring that the chips remain securely attached throughout their operational lifespan.
The composition of rework underfill adhesives typically includes epoxy resins, curing agents, and fillers. These components work together to create a material that not only adheres effectively to both the chip and the substrate but also possesses excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. Additionally, many modern formulations are designed to be low-viscosity, allowing for easy dispensing and ensuring complete coverage of the chip area during application.
Application techniques for rework underfill adhesives vary, but common methods include capillary flow and selective dispensing. During the application process, care must be taken to ensure that the adhesive fills all gaps without leaving voids, as voids can compromise performance and lead to failure. Proper curing is also essential, as it influences the adhesive’s final properties. Depending on the formulation, curing can be achieved through heat or UV light, with each method offering its own set of advantages.
In summary, the use of rework underfill adhesive for chips is essential for maintaining the performance and reliability of semiconductor devices. These adhesives not only facilitate chip rework but also provide critical protection against thermal and mechanical stresses, ultimately extending the life of electronic components. As technology evolves, the importance of high-quality adhesives in chip manufacturing will only continue to grow, making understanding their properties and applications crucial for industry professionals. By leveraging the benefits of rework underfill adhesives, manufacturers can enhance the durability and functionality of their semiconductor devices.
At its core, rework underfill adhesive is designed to support the bond between semiconductor chips and their substrates. This adhesive is particularly crucial during the rework process, which involves repairing or replacing chips without damaging the surrounding components. The ability to remove and replace chips efficiently while maintaining structural integrity is where rework underfill adhesives shine.
One of the primary advantages of these adhesives is their ability to mitigate thermal and mechanical stress. When chips are soldered to substrates, they experience temperature fluctuations and mechanical forces that can lead to delamination or cracking. Rework underfill adhesives provide a protective layer that absorbs these stresses, ensuring that the chips remain securely attached throughout their operational lifespan.
The composition of rework underfill adhesives typically includes epoxy resins, curing agents, and fillers. These components work together to create a material that not only adheres effectively to both the chip and the substrate but also possesses excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. Additionally, many modern formulations are designed to be low-viscosity, allowing for easy dispensing and ensuring complete coverage of the chip area during application.
Application techniques for rework underfill adhesives vary, but common methods include capillary flow and selective dispensing. During the application process, care must be taken to ensure that the adhesive fills all gaps without leaving voids, as voids can compromise performance and lead to failure. Proper curing is also essential, as it influences the adhesive’s final properties. Depending on the formulation, curing can be achieved through heat or UV light, with each method offering its own set of advantages.
In summary, the use of rework underfill adhesive for chips is essential for maintaining the performance and reliability of semiconductor devices. These adhesives not only facilitate chip rework but also provide critical protection against thermal and mechanical stresses, ultimately extending the life of electronic components. As technology evolves, the importance of high-quality adhesives in chip manufacturing will only continue to grow, making understanding their properties and applications crucial for industry professionals. By leveraging the benefits of rework underfill adhesives, manufacturers can enhance the durability and functionality of their semiconductor devices.
Related Information

 China:+86 13509643690
China:+86 13509643690